Navic: Indian GPS System
Satellite Navigation (SATNAV) has revolutionized the navigation world, opening new opportunities which require high precision positioning and timing. Large service volume and all-weather capability provide various applications. Under satellite navigation, SAC works on IRNSS – Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System and the GAGAN systems. IRNSS aims to provide Standard Position Services (SPS) and Restricted Services (RS) for particular users.
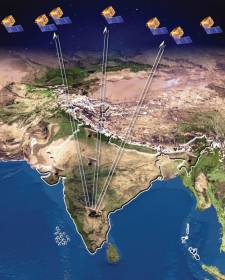
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) is the independent regional navigation satellite system that India developed. It is designed for providing accurate position information service to the users in India and the region that extends up to 1500 km from its boundary, which is its primary service area. IRNSS will provide a position accuracy of finer than 20 m.

IRNSS User receivers being developed by SAC provide timing and position information using signals broadcast by IRNSS Satellites and form the basis for various IRNSS applications, including civil aviation applications.
India has recently introduced its own navigation satellite system developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It is called Navigation With Indian Constellation, abbreviated as NavIC. It ensures accurate location positioning to users in India and neighboring regions.
Qualcomm recently launched new chipsets that support NavIC, including Snapdragon 720G, Snapdragon 662, and the Snapdragon 460. These chipsets come with support for dual-frequency — L1 (1.58 GHz) and L5 (1.17 GHz) — Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS).
Since the app works on the L5 band S-band (2.5 Hz), these chips are designed to support the NavIC standard out of the box automatically. Snapdragon 865 and 765 have the NavIC tracking unit, but it has not been enabled yet.
How to check if your smartphone can support NavIC or not:
Given below will be a step-by-step guide to see if your smartphone has NavIC support or not.
- Install either GSPTest or GNSSTest apps on your Android. You can also install both of them to check out your support for NavIC.
- Once you have installed the app, click on ‘Start Test.’
- The app will then start detecting all the navigation satellites available.
- If the app shows Indian satellites, it means your smartphone can support NavIC.
This is the easiest way currently to know whether or not your smartphone can support NavIC. Not many devices can support this feature, but as more and more devices are released, they will be released with chipsets to handle the smartphone’s feature.
ISRO in India has designed the regional geo-positioning system to provide accurate positioning in India and across the Indian mainland. It is said as more accurate than GPS.
The requirement for an indigenous satellite navigation system was felt when Pakistani troops took their positions in Kargil in 1999. The Indian military sought the global positioning system (GPS) data of the region from the US. However, the military was denied this information, and it was then realized that the importance of an indigenous satellite navigation system was needed.
Planning of this satellite system has been going on for quite some time, and the satellite system was announced first in 2007 and was meant to be functional entirely in 2012, but it did not happen due to various factors which held back the release date. The first of the seven satellites were sent to orbit only in 2013.
According to ISRO, the Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS) was developed for terrestrial, aerial, and marine navigation. It would also help a lot with disaster management and vehicle tracking. It would provide a Standard Positioning Service (SPS) to all users and provide a Restricted Service (RS), an encrypted service for only authorized users. It was then made mandatory for all commercial vehicles in India in 2019.

It is extremely accurate as it has seven satellites; three of them are in geostationary orbit across the Indian Ocean and 4 in geosynchronous orbit. This puts it at par with US-based GPS, Russia’s Glonass, and Europe’s Galileo. The IRNSS is expected to provide a better than 20-meter position accuracy in the primary service area.
On the other hand, 24 satellite-based GPS-enabled smartphones can be accurate within 4.9 meters. In some of the GPS receivers, the accuracy can be up to 11.8 inches. However, it is said that NavIC uses S and L bands, unlike GPS, which only uses L bands. This is supposed to help NavIC be more accurate than GPS.
Qualcomm has created three chipsets with NavIC support, which means more phones may be launched soon in India with NavIC support. Chinese handset maker, RealMe has launched a 5G smartphone model named RealMe X50 Pro, which provides the NavIC system.
Even Chinese tech major Xiaomi said it would bring NavIC technology to their smartphones. It is capable because of Qualcomm Technologies Inc, which is enabled on several of their Qualcomm Snapdragon Mobile Platforms and available across multiple Xiaomi smartphones.
Some of the key consumer applications of NavIC for mobile include precise location mapping in remote, difficult to access areas, precise timing, and visual and voice navigation for drivers.
Therefore, this Navigational Satellite System is a great pride for Indians as it is the first indigenous Navigation System launched. This Navigational System has been in the making for many years, and now it has finally come to fruition. It is being acknowledged and celebrated as it is a great step for India and our Navigation Systems.
Though it has not been widely used yet since most phone systems do not support it, it will be in the future since more phone brands are signing up to have the Navigational System on their phones. Therefore, the landscape of navigation and easy commuting will become different from what we know from now on, which is extremely pleasing and exciting news for India and ISRO.










Comments closed.